What is Acne?
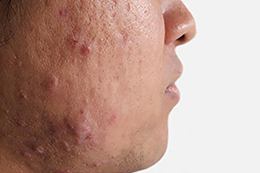
Acne is a condition in which skin becomes oily, and open and closed comedones (blackheads and whiteheads) appear on the face and often the neck, shoulders, chest and back too.
In moderate and severe acne, skin becomes reddened and inflamed papules and pustules develop. It can be emotionally distressing, annoyingly persistent and lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) and/or long-term scarring.
Non-inflammatory forms of acne, like whiteheads and blackheads, occur primarily on the face (forehead, nose and cheeks) and, more rarely, on the back. This form of acne is considered mild. They develop when comedones occur, which is when a hair follicle becomes clogged with oil and dead skin cells.
Inflammatory acne such as pimples, nodules and cysts, occur primarily on the face (forehead, nose and cheeks) and, more rarely, on the back, and, depending on its frequency, can be considered mild or even a moderate form of acne.
While acne may show up in different severities and variations for different people, all acne sufferers agree that they can be unsightly and even painful, and, so, figuring out how to treat acne becomes a priority.



